Featured Research
Macroeconomic Insights: Gold’s New Inflation Playbook
Gold has stopped trading as a clean derivative of US real yields and now reflects a broader external pricing regime. Since 2022, the real-yield anchor has weakened, gold has lined up more consistently with broad-dollar moves, and episodes of dollar tightening have...
Macroeconomic Insights: Gold’s New Inflation Playbook
Gold has stopped trading as a clean derivative of US real yields and now reflects a broader external pricing regime. Since 2022, the real-yield anchor has weakened, gold has lined up more consistently with broad-dollar moves, and episodes of dollar tightening have coincided with more synchronized depreciation within a basket of emerging-market currencies. Inflation outcomes also show episodic fragmentation. Dispersion widens sharply during the 2021–22 shock, compresses through 2023–24, and then widens around 2025. The figures below trace this rotation in drivers and show how it propagates into inflation through exchange rates, tradables pricing, and country-specific pass-through.
The breakdown of the real yield anchor
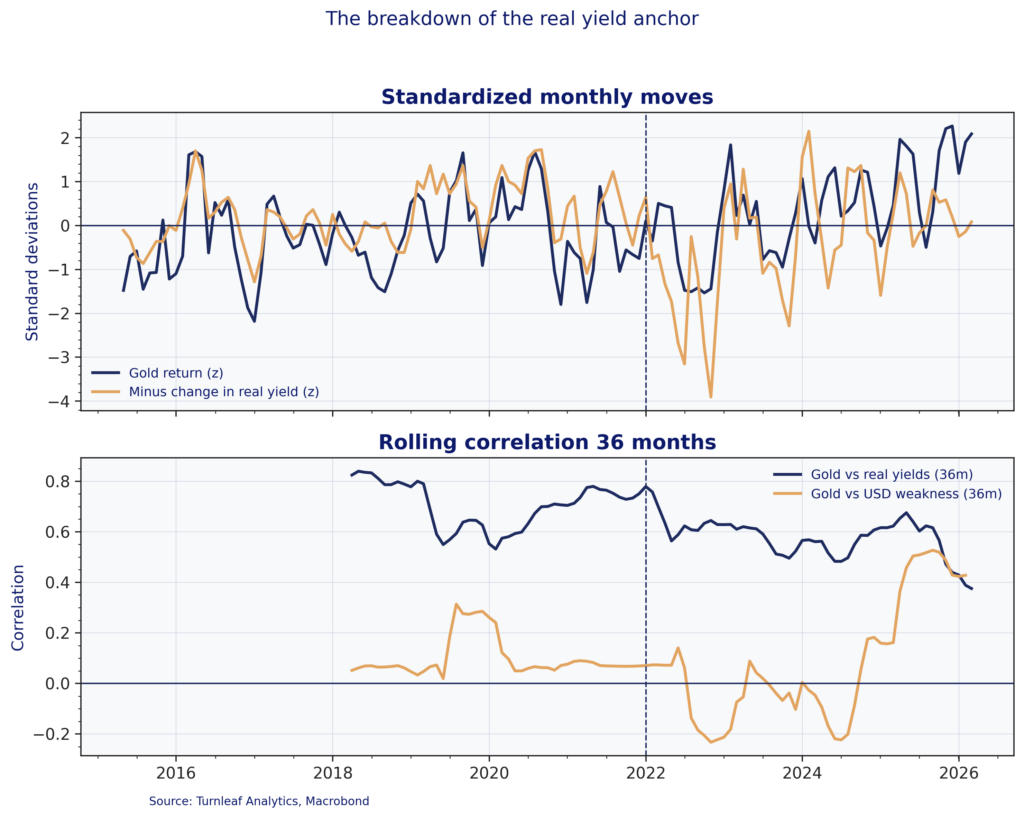
For much of the past decade, real yields offered a reliable framework for thinking about gold. When inflation-adjusted returns on safe assets fell, gold typically benefited. Since 2022, that relationship has weakened. US 10-year real yields rose sharply to post-GFC highs, yet gold remained resilient and went on to set successive record highs through 2025. Figure 1 captures the shift. The rolling correlation between gold and real yields trends lower after 2022, while the correlation between gold and broad-dollar weakness rises into 2025, which is consistent with gold rotating from a rate-dominated signal toward a more FX-sensitive regime.
Emerging-market central banks have helped drive this decoupling by diversifying reserves away from dollar assets. Their buying changes the marginal source of demand and shifts the transmission mechanism. Gold increasingly responds through exchange rates and import-price dynamics via the cost of dollars and local-currency purchasing power, rather than primarily through the domestic real-rate channel.
Figure 1
The dollar channel and EM currency clustering
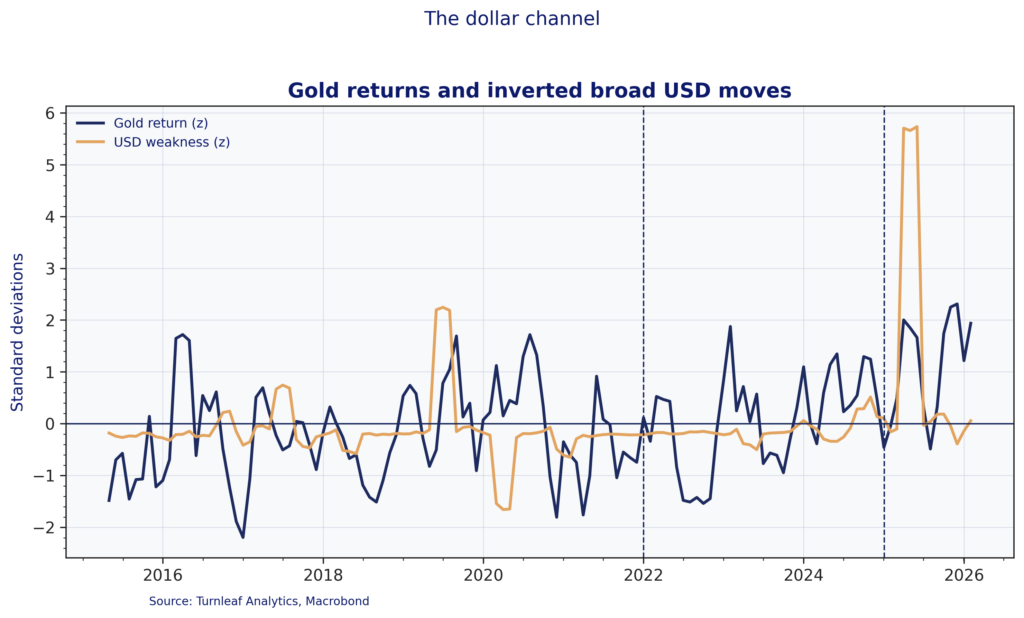
In the current regime, gold strength often lines up with broad-dollar weakness because exchange-rate moves pass through quickly into traded goods and import prices. Figure 2 shows this by plotting gold returns against an inverted broad-dollar index return series. The relationship is episodic, but the co-movement becomes more visible in stress windows, including the large dollar move around the 2025 marker.
Figure 2
For emerging markets, the key issue is synchronicity within the basket rather than idiosyncratic single-country moves. Figure 3 pairs standardized broad-dollar index returns with an EM depreciation basket and a breadth measure that tracks how many currencies in this basket depreciate at the same time. Breadth stays low in most months but rises in stress episodes, which captures the clustering mechanism in practice: the distribution shifts toward shared drawdowns when the broad-dollar strengthens and funding conditions tighten.
Figure 3
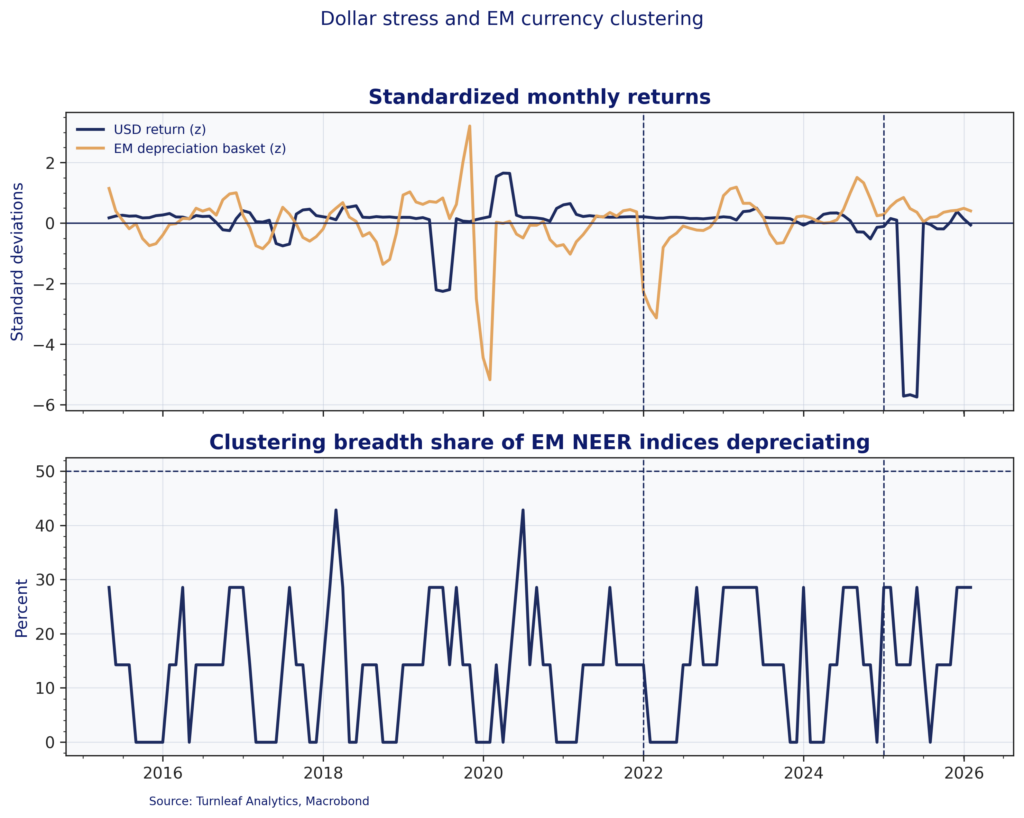
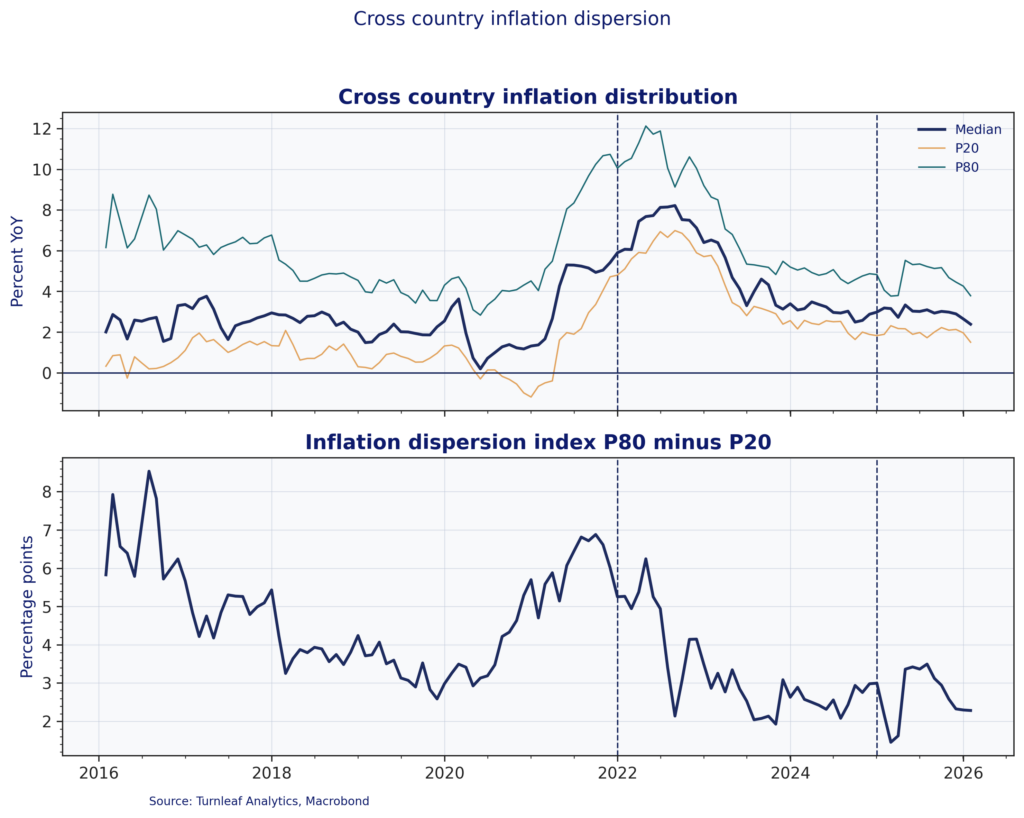
Figure 4 checks whether the shift in transmission shows up in realized outcomes by plotting the cross-sectional distribution of headline CPI inflation across the sample and a trimmed dispersion metric defined as the P80–P20 spread. The sample combines advanced economies and major emerging markets (United States, Eurozone, United Kingdom, Japan, Canada, China, India, Brazil, Mexico, Turkey, South Africa). Dispersion rises into the 2021–22 inflation shock as inflation outcomes fan out across countries, then compresses sharply through 2023 and 2024 as inflation re-converges. The modest widening around 2025 suggests renewed fragmentation, but at a far smaller scale than 2022.
Figure 4
Country-level transmission
The shift from yield-driven to reserve-driven gold increases the scope for inflation dispersion based on structural archetypes.
China is a structural contributor. The PBoC has been an important contributor to the current regime through price-insensitive gold accumulation to reduce exposure to US Treasuries. While domestic inflation in China is muted by capital controls and managed exchange rates, reserve diversification affects the marginal demand for dollars and reshapes global pricing conditions for other economies.
Turkey illustrates regime-dependent pass-through. Turkey’s exchange rate is not a clean market price, because policy has often leaned on reserves, regulation, and administrative measures to smooth or delay depreciation. That does not remove pass-through, it changes its timing and its form.
To read the rest, consider subscribing to Turnleaf’s Substack, here.
Research Archive
Macroeconomic Insights: Israel CPI – Air Travel Expected to Bump Up August Print
On August 3, 2025, Ben Gurion Airport will resume over 120 international flights for the month, though this remains insufficient to fully meet demand. Israeli travel companies...
Macroeconomics Insights: Europeans Can Finally Buy An Apocalypse Hellfire at 0% Tariff
Recently Trump announced a trade deal with the EU with terms that impose a 15% tariff on all E.U. imports (including motor vehicles) and a 0% retaliatory tariff on the U.S....
Macroeconomic Insights: U.S. Core CPI – Who’s Paying for the Tariffs?
In the first five months of 2025, the U.S. government collected $68.9 billion in tariffs and excise taxes, as the Yale Budget Lab reports the effective tariff rate surged from...
Macroeconomics Insights: Navigating Inflation and Deflation – China and Japan
As we approach the second half of 2025, the inflation trajectories of China and Japan reflect contrasting dynamics shaped by domestic economic conditions, external influences,...
Run to Research
Left foot forward, right foot forward, puncturing the mud, plodding along, the wind in winter, the sun in summer, in the trees’ shadows, patterns of light and dark along the...
Macroeconomic Insights: Ea-Nasir’s Fine Quality Copper Hit with 50% Tariffs in August
Since the inauguration of President Trump, uncertainty has significantly influenced inflation dynamics, primarily through unpredictable tariff policies. However, firms are now...
Macroeconomic Insights: United States CPI – Firms are Still Front-Loading
To date, uncertainty has been the defining feature of the inflation story. Volatile trade policy has deterred many firms from making strategic investments, slowing business...
Macroeconomic Insights: FX, Oil, Copper, and Tariff Risks in Emerging Markets
Across Colombia, Chile, Brazil, and China, inflation dynamics are currently shaped by common external themes: exchange rate movements, global commodity prices—particularly...
Twenty years in financial markets
Time is a curious thing. We say time passes, yet rather than simply pass, time tends to dissolve. Once gone, it dissolves leaving an imprint behind. At times, it's a clear...
Macroeconomic Insights: Czech Republic CPI – House Prices on the Rise
Recently, housing prices in the Czech Republic have increasingly exerted upward pressure on inflation. Our June 2025 Forecast Word Cloud highlights the primary drivers...
Macroeconomic Insights: Malaysia CPI – Electricity Tariff Reform from July 2025
Malaysia has changed its electricity tariff schedule, and allegedly, it should save the average consumer up to 19% on their bills. However, after an announcement in June 2025,...
Macroeconomic Insights: Hungary CPI – Food Prices on the Rise
At the end of May 2025, the Orban government decided to extend the profit margin cap on 30 essential food items through August 2025, in line with previous guidance stating the...
Macroeconomic Insights: Vegetable Prices Push India Inflation Downwards
In 2024, volatile vegetable prices repeatedly triggered in-market releases from India’s Price Stabilisation Fund (PSF). PSF, launched in 2014–15, was designed to curb extreme...
Macroeconomic Insights: Israel CPI – The Cost of War
Over the past 24 hours, Israel’s strike on Iran has markedly increased upside risks to inflation in the country. Just as tariffs introduce additional costs to consumers,...
Macroeconomic Insights: Spain CPI – Is it Time to Buy a House?
Since the start of the year, housing market indicators have increasingly correlated with rising inflation pressures. Interestingly, Spain classifies mortgages as financial...