Featured Research

Macroeconomic Insights: South Africa CPI – When Currency Strength Meets Energy Vulnerability
After trending downward through most of 2025 alongside rand appreciation and falling oil prices, Turnleaf’s 12 month inflation forecast for South Africa is now pointing at rising inflation pressure in 2026 (Figure 1). Rebounding oil prices are overwhelming the...
Macroeconomic Insights: South Africa CPI – When Currency Strength Meets Energy Vulnerability
After trending downward through most of 2025 alongside rand appreciation and falling oil prices, Turnleaf’s 12 month inflation forecast for South Africa is now pointing at rising inflation pressure in 2026 (Figure 1). Rebounding oil prices are overwhelming the disinflationary benefits of a stronger currency, exposing South Africa’s structural vulnerability in energy markets.
Figure 1 – (to see Turnleaf’s 12-month forecast for South Africa, visit our latest Substack post, here)
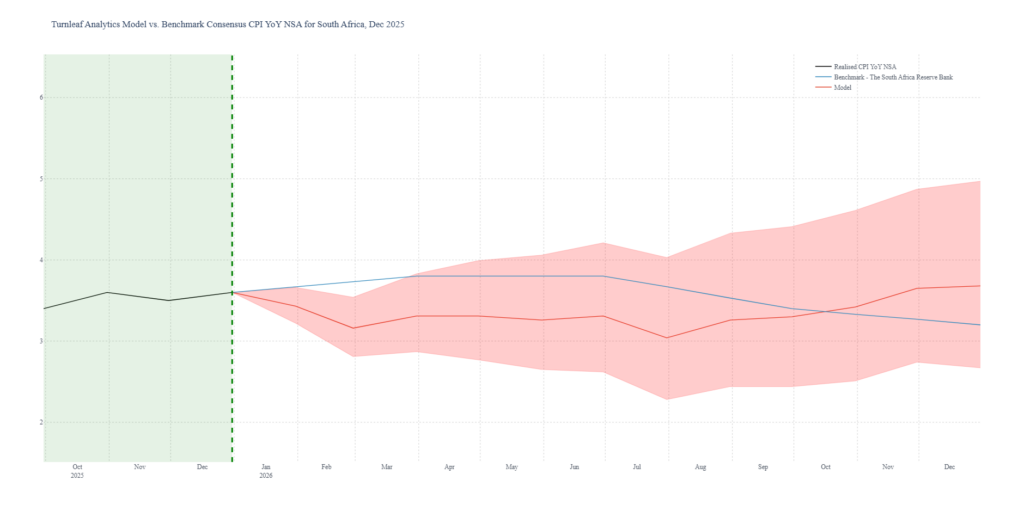
While currency appreciation against the dollar provides relief on import costs, the country’s near-total dependence on imported oil creates a direct transmission channel from global energy markets into domestic prices—one that operates faster and more forcefully than the gradual benefits of rand strength. When oil prices turn upward, as they have since late 2025, South Africa’s energy sector becomes the dominant inflation driver, regardless of what’s happening with the exchange rate.
The Currency Cushion: Real But Limited
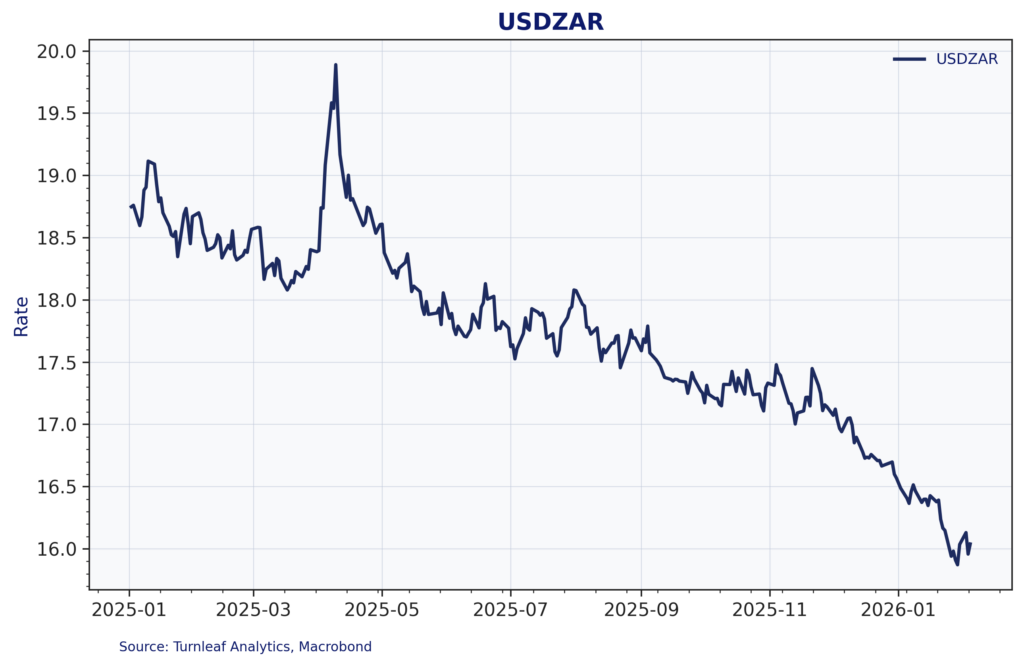
The rand’s performance through 2025 was remarkable. Figure 2 shows the USDZAR exchange rate declining from around 19 rand per dollar in early 2025 to approximately 16 rand per dollar by early 2026—a substantial appreciation of roughly 16%. This strengthening reflects both broad USD weakness amid geopolitical uncertainty and South Africa-specific factors, particularly the country’s position as a major gold producer during a period of surging gold prices.
Figure 2: USDZAR Exchange Rate
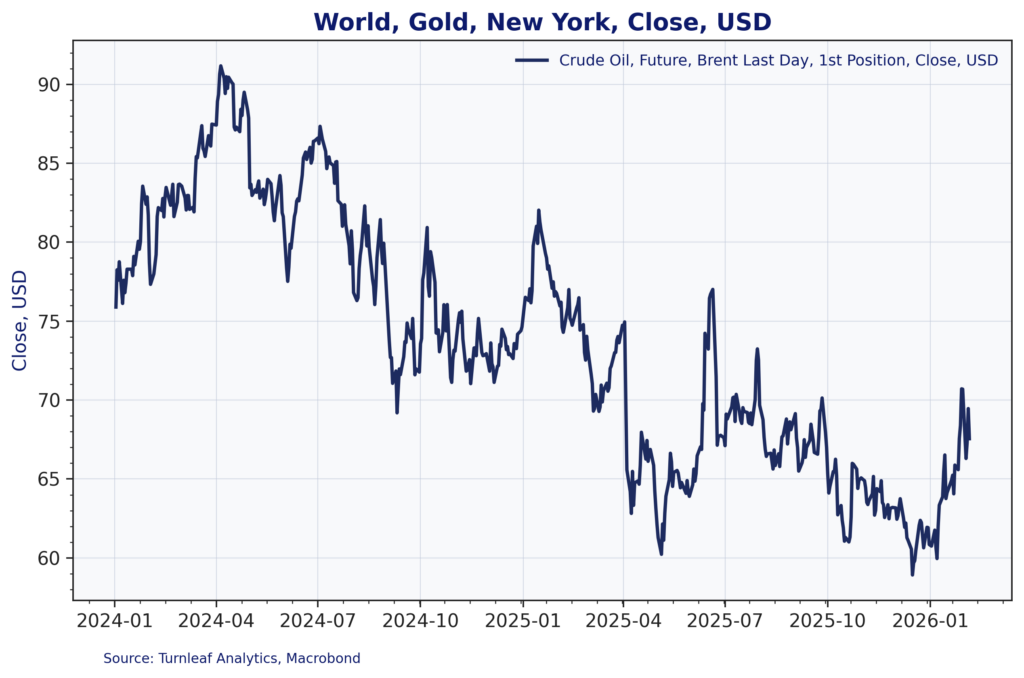
Gold’s role here deserves attention. Figure 3 shows gold prices surging from around $2,000 per ounce in early 2024 to a peak above $5,400 in late 2025, driven by the metal’s emerging role as an alternative reserve asset in global financial transactions. While gold has since pulled back to around $4,800 per ounce in early February 2026, the sustained elevation in prices has delivered a substantial windfall to South Africa’s mining sector and export revenues.
Figure 3: Gold Prices (USD/oz)
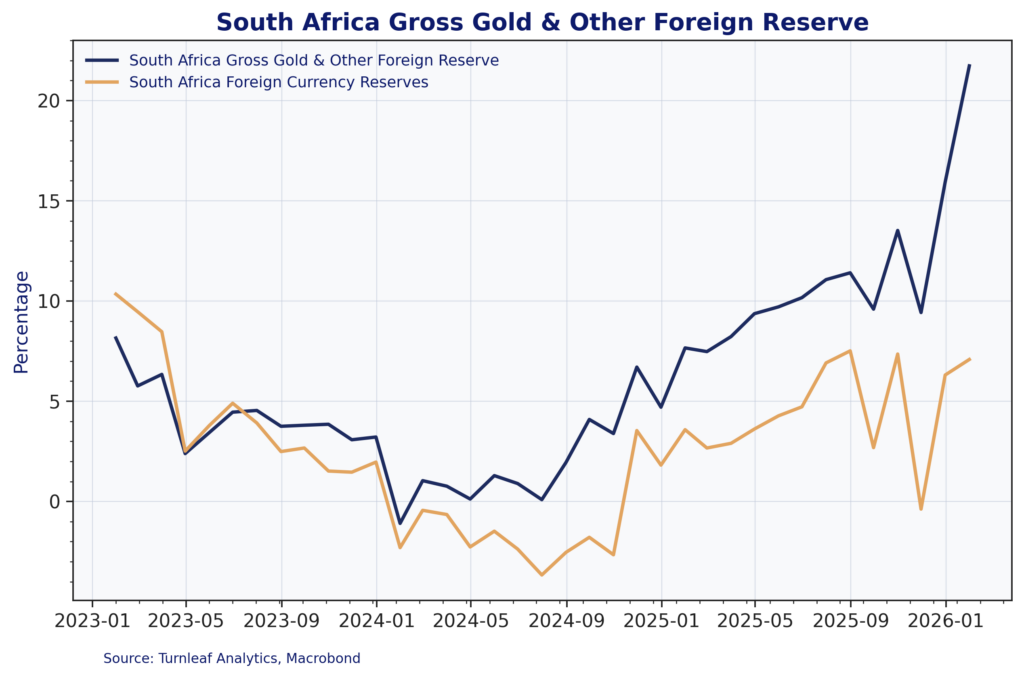
This gold windfall strengthened South Africa’s external position in measurable ways. Figure 4 shows gold and other reserves increasing sharply as a share of total reserves, rising from around 10% to over 21% by early 2026, while traditional foreign currency reserves remained relatively stable. This reserve accumulation has provided the South African Reserve Bank with greater policy flexibility and reduced the near-term pressure for currency intervention.
Figure 4: South Africa Reserve Composition
The combination of USD weakness, gold export revenues, and reserve accumulation has given South Africa breathing room on the currency front. Rand appreciation naturally reduces import costs and provides disinflationary support. But this cushion proves insufficient when set against the country’s structural energy vulnerabilities.
The Energy Transmission: Fast and Forceful
South Africa’s inflation vulnerability centers on oil, not because of any particular policy failure but because of unavoidable geography and infrastructure constraints. The country imports approximately 95% of its petroleum consumption, with international crude prices—denominated in USD—accounting for roughly 50% of domestic fuel costs. This creates a direct, rapid transmission from global oil markets to South African consumer prices through the monthly fuel price adjustment mechanism.
International oil prices have moved dramatically over the past two years. Figure 5 shows Brent crude peaking near $90 per barrel in mid-2024, then declining substantially through 2025 to reach lows near $60 per barrel in late 2025. This extended decline provided significant disinflationary relief and contributed to the downward trend in our inflation forecasts through most of 2025.
Figure 5: Brent Crude Oil Prices (USD/bbl)
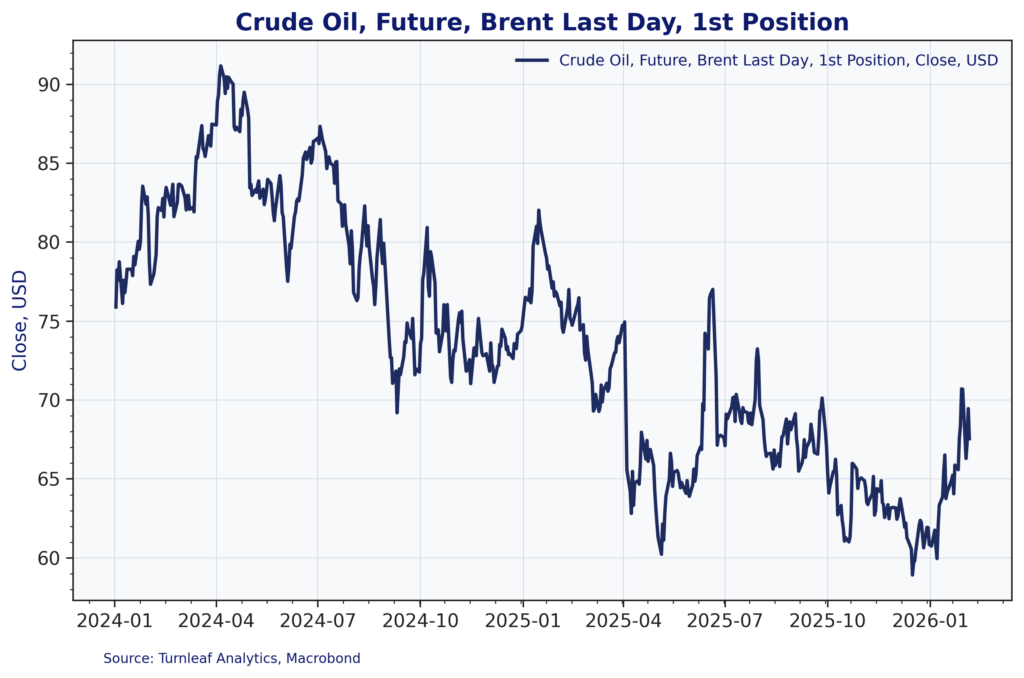
But the oil story has reversed. Brent crude has rebounded from its late-2025 lows and is now trading back toward $70 per barrel in early 2026. This $10 increase, while modest in absolute terms, matters enormously for South African inflation because it operates through a direct, mechanical transmission channel with minimal lags.
Figure 6 illustrates the domestic impact. South African gasoline prices rose from around 14-15 rand per liter in 2020-2021 to peaks above 26 rand per liter in 2023, before moderating to around 20-21 rand per liter in early 2026.
Figure 6: South Africa Gasoline Prices (ZAR/liter)
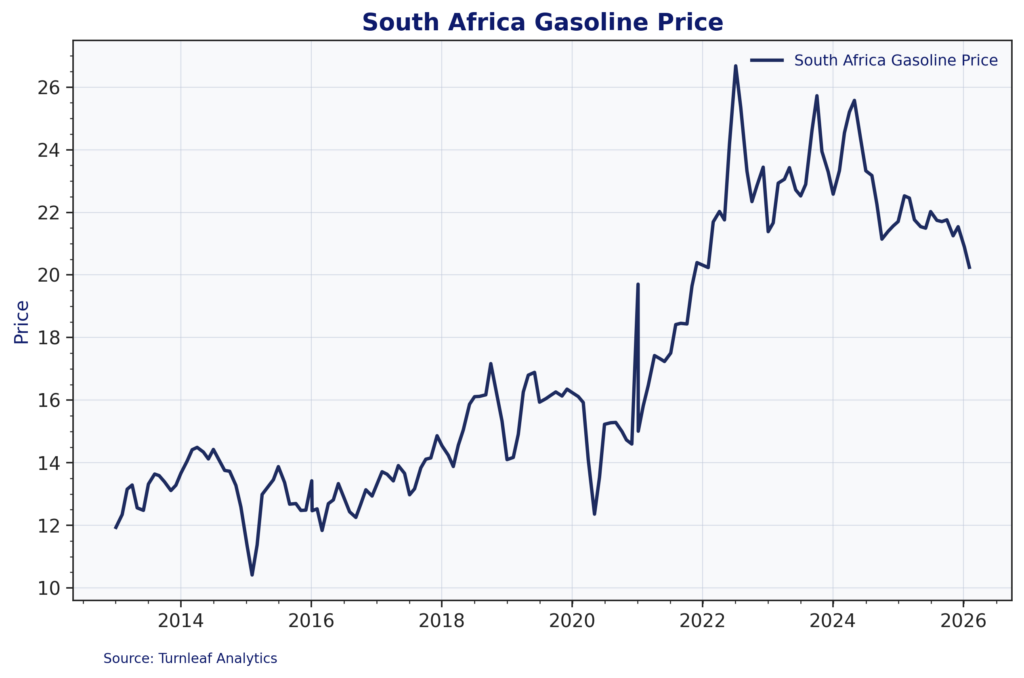
The monthly adjustment mechanism means any movement in international oil prices or the USDZAR exchange rate translates quickly into pump prices. Even as rand strength provides some offset, rising crude prices feed through rapidly.
The oil transmission extends beyond direct fuel costs into the electricity sector, amplifying the inflationary impact. Eskom, South Africa’s state-owned utility, relies on coal for 80-90% of generation but must turn to diesel-powered backup generation during peak demand periods or when coal units fail. This diesel dependency creates a direct link between global oil markets and electricity costs, adding a second transmission channel for oil price movements.
Recent improvements in Eskom’s operational performance—including better coal unit reliability and reduced diesel consumption—have moderated this channel somewhat. Reports from early 2026 indicate meaningful progress in energy capacity performance. However, these operational improvements, while welcome, do not eliminate South Africa’s fundamental energy vulnerability. The direct fuel price channel remains dominant, and any significant oil price increase will flow through to inflation regardless of marginal improvements in Eskom’s diesel consumption.
Please see our Substack for the rest.
Research Archive
Turnleaf Forecast Review: Recent Misses and Outcomes
This issue aims to clarify several of Turnleaf’s and the market’s forecast deviations over the past few months. Below, we outline key insights and performance drivers across a...
Macroeconomic Insights: India’s Inflation Paradox – Headline Drops, Core Rises
In recent forecasts, Turnleaf has observed an interesting trend in India’s inflation dynamics. While headline inflation has been trending downward, largely driven by a decrease...
Macroeconomic Insights: Polish Inflation – What Could Be, What Won’t Be in 2025
Recent retail sales in Poland have come in below expectations (-0.5%YoY in February 2025), with a significant decline driven by vehicle sales, followed by reduced consumption in...
Macroeconomic Insights: Mexico’s Inflation Path In Tariff Uncertainty Limbo
The tail of our inflation curve is currently driven by two key factors: U.S. tariffs set for April 2, 2025, and Plan Mexico, which aims to revitalize domestic manufacturing and...
Macroeconomic Insights: How Germany’s Fiscal Stimulus Could Reshape Its Inflation Outlook
Amid shifting geopolitical tensions and the need to revitalise its economy, Germany is preparing for a massive fiscal stimulus that will allocate up to $1 trillion in defence and...
Emerging Markets: Turnleaf Discusses Impact on Hungary’s 10% Profit Margin Cap Restriction on Inflation
Policy: In Hungary, from March 17 to May 31, 2025, a 10% profit margin cap will be imposed on 30 essential products, limiting companies' profits on these items. Small independent...
Macroeconomic Insights: U.S. Inflation is Coming, But Not Where You Expect
Since taking office, President Trump has aggressively worked to revitalize domestic manufacturing by focusing on the U.S. trade balance. A key part of this strategy has been...
Learning from running financial models live
Let's say you are the world's best burger chef (we all have ambitions, right). You'd be serving up all manner of burgers for your customers. It would be odd though, wouldn't it,...
Macroeconomics Insights – Beyond Tariffs: How Uncertainty is Steering U.S. Inflation Expectations
When we forecast inflation, our goal is to account for as much explainable variation as possible, using available data and reasonable assumptions about how prices evolve....
Macroeconomic Insights: Tariffs, Manufacturing, and Mexico Inflation
This article marks the start of Turnleaf’s series on how U.S. tariffs shape inflation dynamics across Latin America (LATAM). Among the economies we monitor—Colombia, Brazil,...
Macroeconomic Insights: How U.S. Tariffs and Eurozone Weakness Are Shaping Chinese Inflation
The trajectory of Chinese inflation will largely depend on its sensitivity to U.S. tariffs and its ability to sustain domestic GDP growth through external demand, particularly...
Macroeconomic Insights: Prices to Increase in February 2025 as Canada’s Tax Holiday Takes a Holiday
Between mid-December 2024 and mid-February 2025, the Canadian government implemented a GST/HST tax holiday, exempting beverages, restaurants, children’s clothing and footwear,...
Macroeconomic Insights: Fueling the Inflation Fire – Turnleaf’s Turkish Inflation Curve Shifts Upwards
Turnleaf’s latest data has pushed Turkey’s inflation outlook higher than consensus forecasts. There are multiple reasons for this which we will explain in this note. One of the...
Macroeconomic Insights: Assessing the Inflationary Impact of U.S. Steel & Aluminum Tariffs
The newly announced 25% tariff on U.S. steel and aluminum imports introduces cost pressures across global supply chains. However, the key question is not just how markets react,...
Emerging Markets: January 2025 Colombia and Hungary CPI YoY Forecast Review
2025 Colombia CPI YoY Above Consensus Due to Global Inflation Pressures Turnleaf’s CPI YoY model projects Colombia inflation well above consensus 12 months out, as it more...