Featured Research
Macroeconomic Insights: Gold’s New Inflation Playbook
Gold has stopped trading as a clean derivative of US real yields and now reflects a broader external pricing regime. Since 2022, the real-yield anchor has weakened, gold has lined up more consistently with broad-dollar moves, and episodes of dollar tightening have...
Macroeconomic Insights: Gold’s New Inflation Playbook
Gold has stopped trading as a clean derivative of US real yields and now reflects a broader external pricing regime. Since 2022, the real-yield anchor has weakened, gold has lined up more consistently with broad-dollar moves, and episodes of dollar tightening have coincided with more synchronized depreciation within a basket of emerging-market currencies. Inflation outcomes also show episodic fragmentation. Dispersion widens sharply during the 2021–22 shock, compresses through 2023–24, and then widens around 2025. The figures below trace this rotation in drivers and show how it propagates into inflation through exchange rates, tradables pricing, and country-specific pass-through.
The breakdown of the real yield anchor
For much of the past decade, real yields offered a reliable framework for thinking about gold. When inflation-adjusted returns on safe assets fell, gold typically benefited. Since 2022, that relationship has weakened. US 10-year real yields rose sharply to post-GFC highs, yet gold remained resilient and went on to set successive record highs through 2025. Figure 1 captures the shift. The rolling correlation between gold and real yields trends lower after 2022, while the correlation between gold and broad-dollar weakness rises into 2025, which is consistent with gold rotating from a rate-dominated signal toward a more FX-sensitive regime.
Emerging-market central banks have helped drive this decoupling by diversifying reserves away from dollar assets. Their buying changes the marginal source of demand and shifts the transmission mechanism. Gold increasingly responds through exchange rates and import-price dynamics via the cost of dollars and local-currency purchasing power, rather than primarily through the domestic real-rate channel.
Figure 1
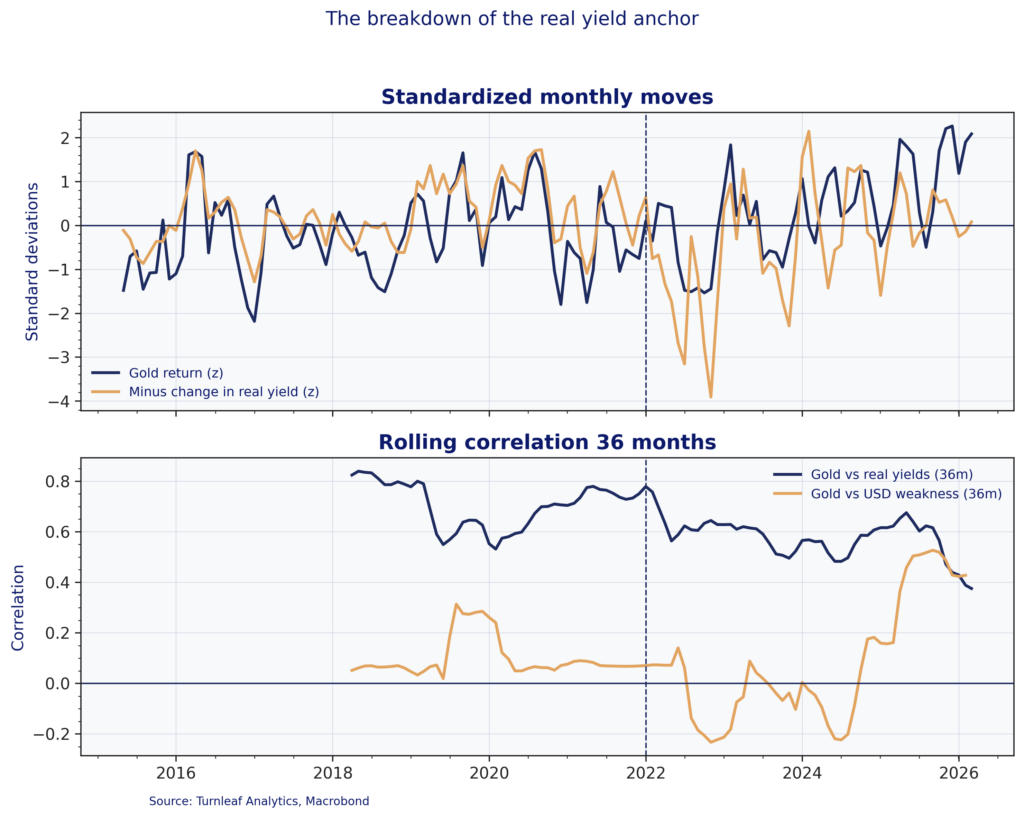
The dollar channel and EM currency clustering
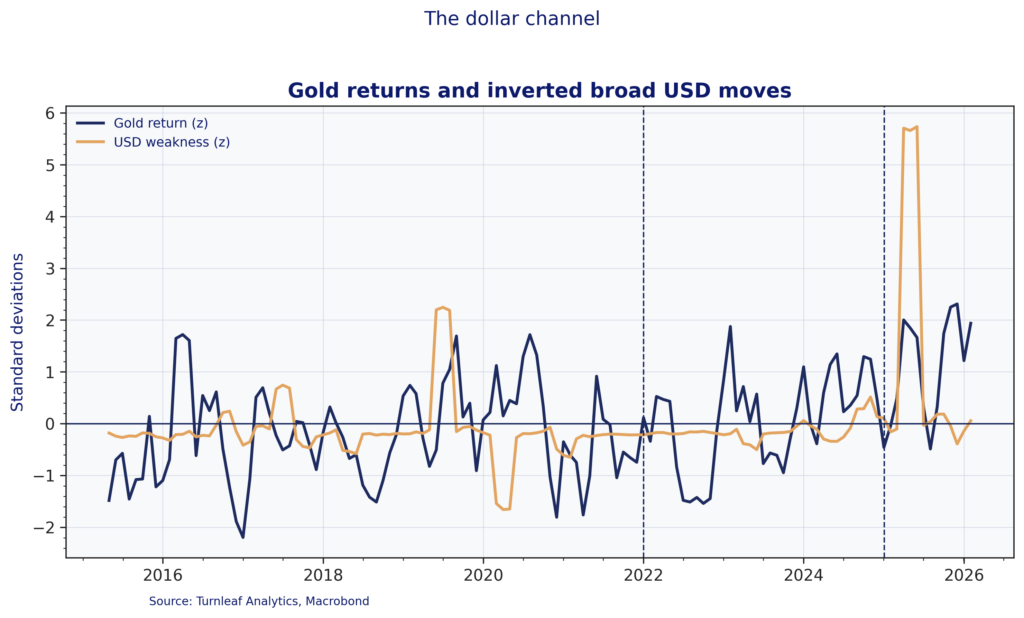
In the current regime, gold strength often lines up with broad-dollar weakness because exchange-rate moves pass through quickly into traded goods and import prices. Figure 2 shows this by plotting gold returns against an inverted broad-dollar index return series. The relationship is episodic, but the co-movement becomes more visible in stress windows, including the large dollar move around the 2025 marker.
Figure 2
For emerging markets, the key issue is synchronicity within the basket rather than idiosyncratic single-country moves. Figure 3 pairs standardized broad-dollar index returns with an EM depreciation basket and a breadth measure that tracks how many currencies in this basket depreciate at the same time. Breadth stays low in most months but rises in stress episodes, which captures the clustering mechanism in practice: the distribution shifts toward shared drawdowns when the broad-dollar strengthens and funding conditions tighten.
Figure 3
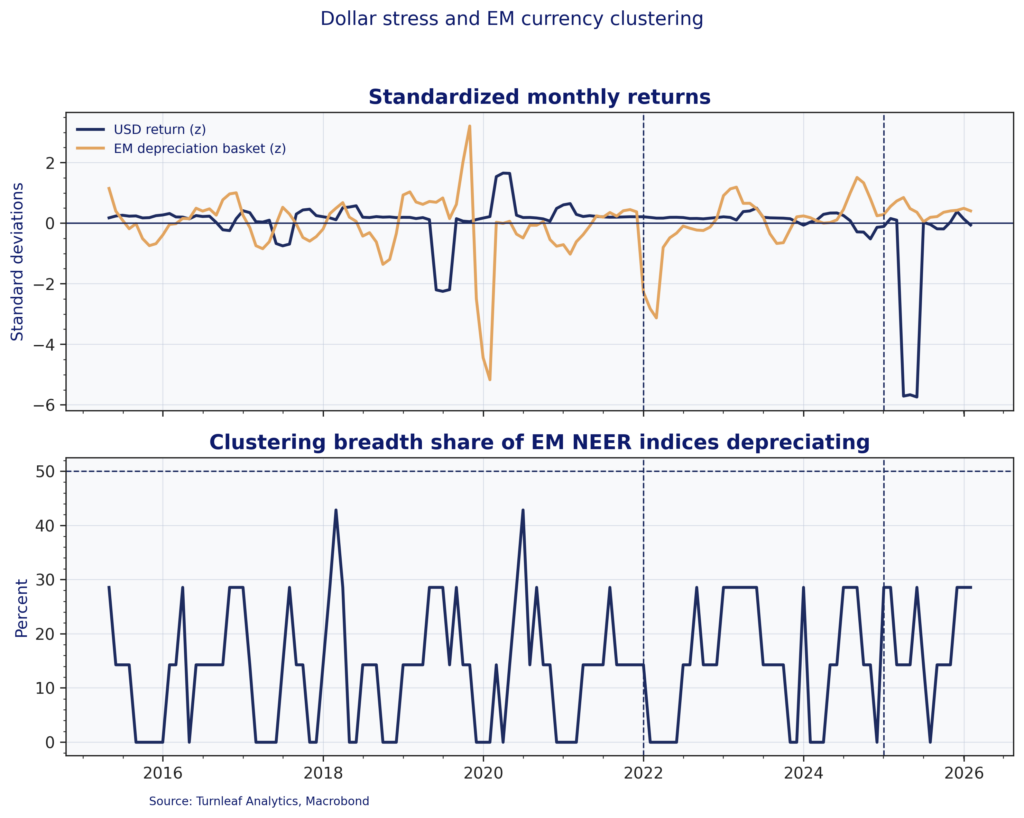
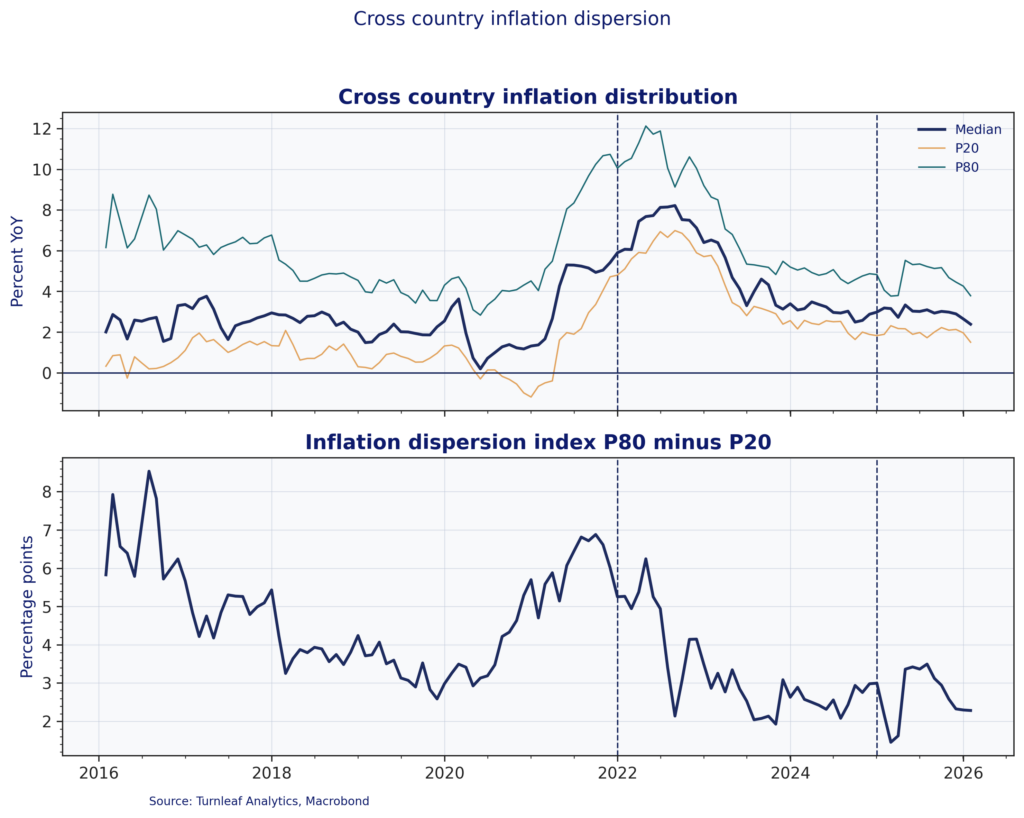
Figure 4 checks whether the shift in transmission shows up in realized outcomes by plotting the cross-sectional distribution of headline CPI inflation across the sample and a trimmed dispersion metric defined as the P80–P20 spread. The sample combines advanced economies and major emerging markets (United States, Eurozone, United Kingdom, Japan, Canada, China, India, Brazil, Mexico, Turkey, South Africa). Dispersion rises into the 2021–22 inflation shock as inflation outcomes fan out across countries, then compresses sharply through 2023 and 2024 as inflation re-converges. The modest widening around 2025 suggests renewed fragmentation, but at a far smaller scale than 2022.
Figure 4
Country-level transmission
The shift from yield-driven to reserve-driven gold increases the scope for inflation dispersion based on structural archetypes.
China is a structural contributor. The PBoC has been an important contributor to the current regime through price-insensitive gold accumulation to reduce exposure to US Treasuries. While domestic inflation in China is muted by capital controls and managed exchange rates, reserve diversification affects the marginal demand for dollars and reshapes global pricing conditions for other economies.
Turkey illustrates regime-dependent pass-through. Turkey’s exchange rate is not a clean market price, because policy has often leaned on reserves, regulation, and administrative measures to smooth or delay depreciation. That does not remove pass-through, it changes its timing and its form.
To read the rest, consider subscribing to Turnleaf’s Substack, here.
Research Archive
Macroeconomic Insights: Hungary CPI Still Has a Long Way to Go
Turnleaf’s September 2025 headline inflation forecast for Hungary over the next 12 months points to an uptick toward 5% YoY by October 2025, followed by a steady decline into...
Macroeconomic Insights: Eurozone CPI – Services Keeping the Economy Running
At the start of 2025, tariffs posed a meaningful downside risk to Eurozone inflation. Yet Eurozone growth has proven more resilient than many expected. The potential loss of...
Gelato and accurate data in markets
I've been subscribing to the FT for many years. Primarily, I read it to keep track of financial markets. FT's longer form pieces complement having access to short articles on...
Macroeconomic Insights: Peru CPI – Seasonality Overshooting Inflation Forecasts
Since May 2025, Peru’s inflation has been consistently undershooting the forecasts of the central bank and economists. Figure 1 shows successive BCRP forecast vintages for...
Macroeconomic Insights: Philippines CPI – Fish Takes a Bite Into Inflation
For the past few months, we have seen our forecasts for the Philippines adjust upwards as the central bank pivots from inflation-defensive to disinflation-offensive. Our...
Macroeconomic Insights: Colombia CPI — Understanding Prices Through the Media
In Colombia, almost 17% of the consumer price basket are administratively set. This includes household public services, transport, fuel, and education fees. The legislation...
Macroeconomic Insights: Energy Prices —The Arbiter of Czech Republic CPI
Turnleaf expects Czech CPI to fall close to 2% YoY by the end of 2025 and then float back up towards 3% YoY through 2026. In the short term, our model places greater weight on...
Macroeconomic Insights: What’s on the Inflation Menu? – Turnleaf’s Food Index Catalogue
In Spain, it’s jamón. In Italy, Parmigiano Reggiano. In Japan, fresh fish. Every country has its culinary treasures, but when the prices of these beloved staples rise, the...
Macroeconomic Insights: Italy and Spain CPI: Unpacking Energy
Understanding how energy costs feed into CPI is crucial for accurately interpreting headline inflation in Europe. Both Spain and Italy offer unique case studies of how specific...
Macroeconomic Insights: South Africa CPI – Inflation and the Rand
Currently, the SARB has revised its forecasts downwards in response to rand appreciation and weaker economic growth. In contrast, Turnleaf’s model paints a more optimistic...
Macroeconomic Insights: Romania CPI Runs Hot
The recent surprise increase in electricity prices in Romania has pushed inflation close to 8%YoY. As Romania begins to rollback inflation fighting policies in the next couple of...
Macroeconomic Insights: U.S. CPI, Evaluating the Impact of Tariffs at Home and Abroad
When evaluating the impact of tariffs on consumer prices, we consider how they affect prices both domestically and abroad. Key factors include the effective tariff rate, the...
Macroeconomic Insights: Switzerland CPI – Just How Much Will Tariffs Hurt Switzerland?
Last week, President Trump threatened to impose a 39% tariff on Switzerland, higher than the initial 31% discussed in April 2025. With the U.S. being a major importer of Swiss...
Macroeconomic Insights: Eurozone CPI – Inflation Running Hotter Than Expected
The Eurozone Grew More Than Expected – Germany & Italy Overall, the Eurozone has enjoyed 0.6%QoQ growth in 2025Q1 despite disinflationary forces like weaker consumer and...
Macroeconomic Insights: Israel CPI – Air Travel Expected to Bump Up August Print
On August 3, 2025, Ben Gurion Airport will resume over 120 international flights for the month, though this remains insufficient to fully meet demand. Israeli travel companies...