Featured Blog
Macroeconomic Insights: A Pinch of Real Rates, a Dash of Slack: Turnleaf’s 2025 U.S. Inflation Recipe
At Turnleaf Analytics, leveraging our machine learning models, we project U.S. inflation to stabilize between 2–3% through 2025, shaped by the interplay of import inflation, expectations, and economic slack, especially with the possibility of new tariffs. Rising...
Macroeconomic Insights: A Pinch of Real Rates, a Dash of Slack: Turnleaf’s 2025 U.S. Inflation Recipe
At Turnleaf Analytics, leveraging our machine learning models, we project U.S. inflation to stabilize between 2–3% through 2025, shaped by the interplay of import inflation, expectations, and economic slack, especially with the possibility of new tariffs. Rising import costs can drive up prices and influence inflation expectations, while economic slack affects how much those costs impact overall inflation. These ingredients, together, form the foundation of our inflation outlook.
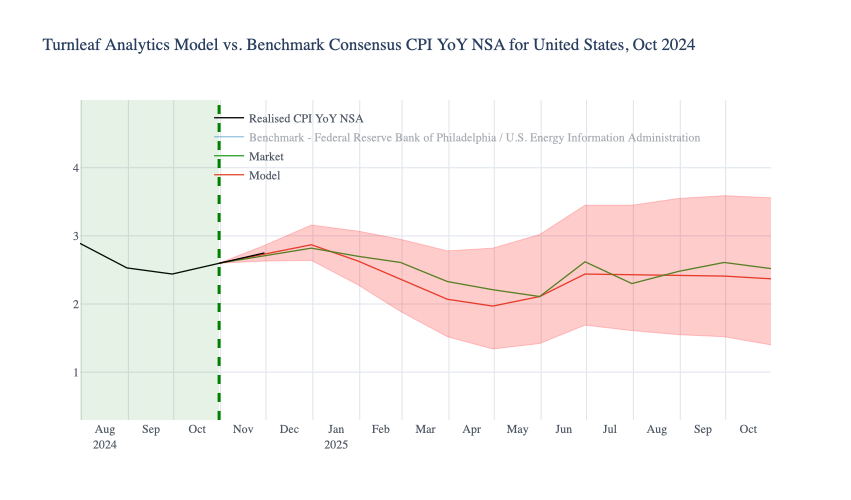 Below, we illustrate how central bank policy rates influence inflation through trade channels. Higher policy rates in the U.S. or Mexico attract foreign investors, strengthening their respective currencies. A stronger currency lowers import costs, reducing inflationary pressures by making goods and materials cheaper. Conversely, lower policy rates weaken currencies, driving up import costs and amplifying inflation.
Below, we illustrate how central bank policy rates influence inflation through trade channels. Higher policy rates in the U.S. or Mexico attract foreign investors, strengthening their respective currencies. A stronger currency lowers import costs, reducing inflationary pressures by making goods and materials cheaper. Conversely, lower policy rates weaken currencies, driving up import costs and amplifying inflation.
This trade-driven mechanism demonstrates how exchange rates serve as a key channel through which monetary policy shapes inflation, particularly in economies reliant on imported goods. Understanding these dynamics is essential for predicting how central bank decisions ripple through global trade networks to influence domestic price levels.
The second graph adds another layer to this story by highlighting the difference in inflation-adjusted policy rates, or real rates. When US real rates are higher than Mexico’s, investors favor the Dollar, leading to a weaker Peso. This weakens Mexico’s ability to contain inflation, as imports become more expensive. Conversely, when Mexico’s real rates are higher, the Peso strengthens, which helps Mexico control inflation but can increase inflationary pressures in the US by making imports more expensive.

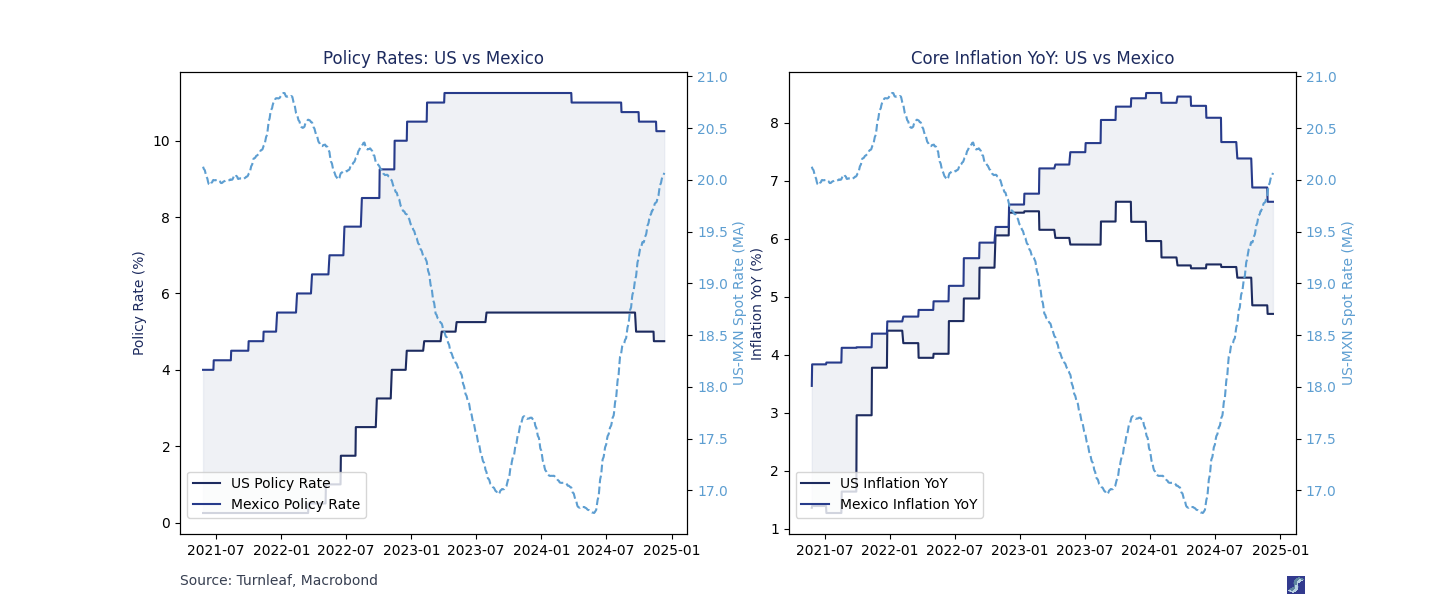
Expectations: Exchange rates, therefore, provide a forward-looking measure of inflation risk. By observing these dynamics, we can better understand the trajectory of future inflation in both countries. A stronger Peso often signals tighter Mexican policies or looser US policies, and vice versa. The Texas Manufacturing Outlook Survey highlights how negative real rates amplify expected raw material costs, reinforcing the link between market expectations, inflation, and exchange rates.
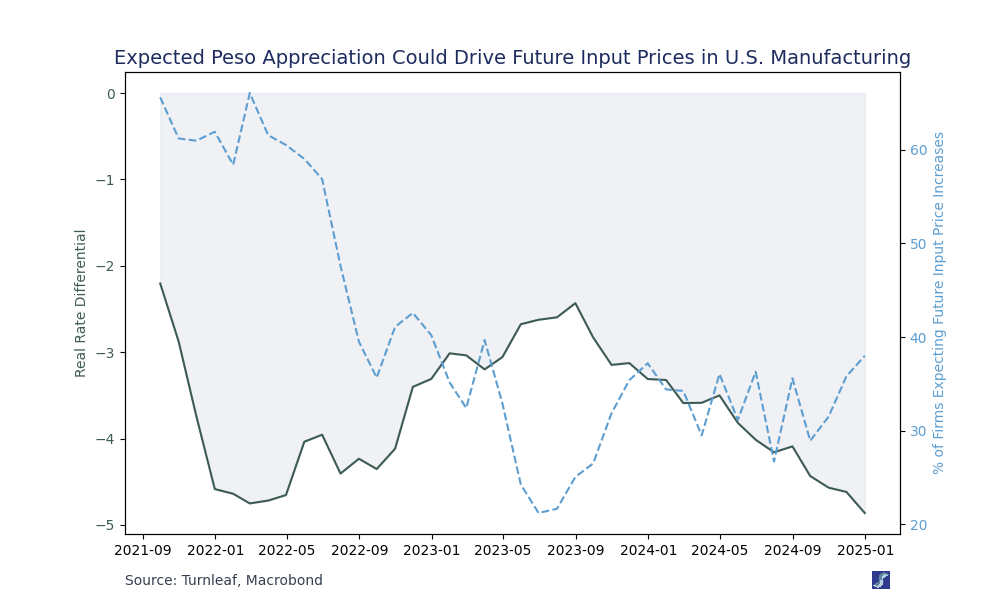
Imported Inflation: Positive interest rate differentials between the U.S. and its trading partners not only help anchor domestic inflation expectations but also support currency appreciation, which can reduce import costs. A notable case is the U.S. dollar’s appreciation against the Chinese yuan following the Fed’s aggressive rate hikes amid a subdued Chinese economy, which eased inflationary pressures on imported goods. For example, as U.S. real rates rise, the dollar appreciates with respect to the Yuan, making metal exports cheaper. When considering imported inflation, adding tariffs could be analogous to increasing China’s real rates, leading to Yuan appreciation and costlier raw material imports for the U.S.. The future of inflation in a tariff world will largely depend on the interplay between real rates between the U.S. and China.
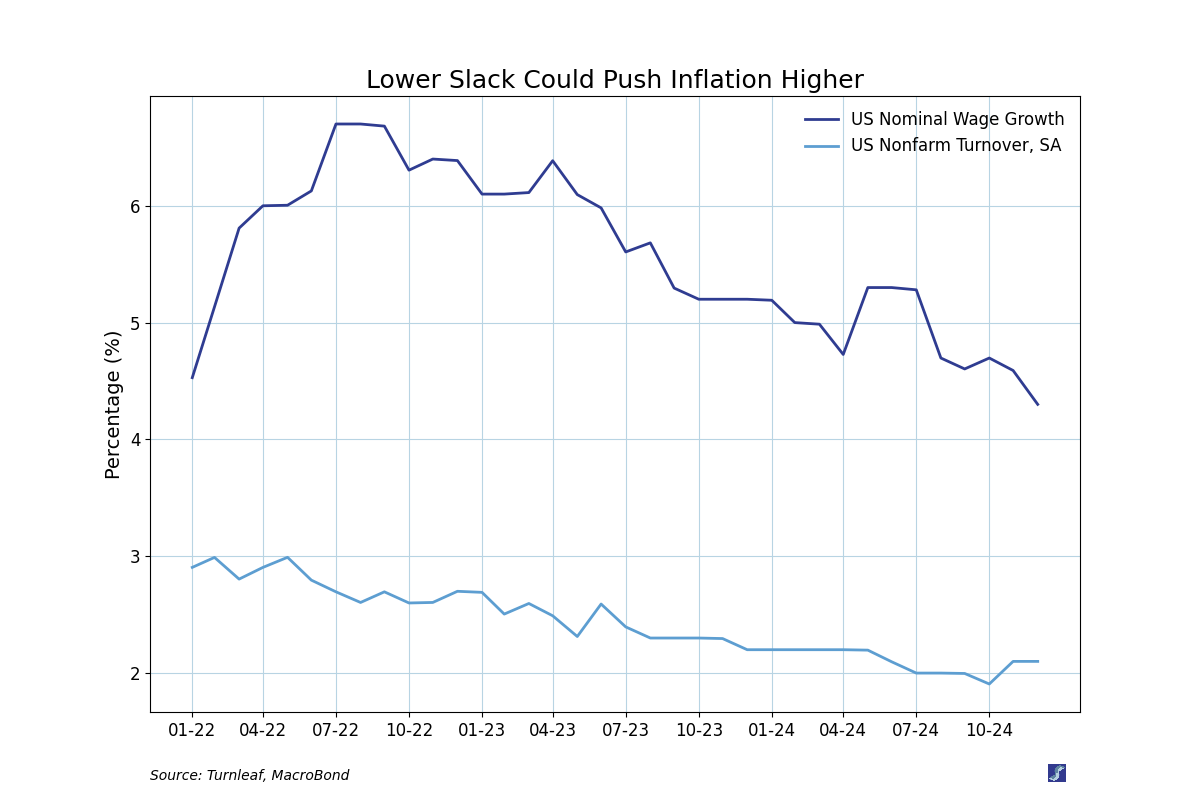
Slack: Lower turnover could indicate that fewer workers are switching jobs due to reduced hiring or preference for greater job stability. At the same time, slowing wage growth suggests a moderation in labor-driven inflation pressures. However, factors such as deportations leading to labor shortages could further reduce slack, tightening the labor supply and potentially driving wage growth higher. This dynamic complicates the relationship between slack and inflation, requiring close monitoring of how these forces evolve in the coming months.
 By analyzing hundreds of interconnected factors within these major groups and by leveraging the power of machine intelligence, we can better interpret the forces shaping inflation and identify the conditions likely to drive future price changes through 2025.
By analyzing hundreds of interconnected factors within these major groups and by leveraging the power of machine intelligence, we can better interpret the forces shaping inflation and identify the conditions likely to drive future price changes through 2025.
Blog Archive
Flash Inflation Outlook: South Korea Inflation Amid Political Instability
South Korea’s brief declaration and subsequent revocation of martial law by President Yoon has damaged investor confidence, further weakening the won and placing pressure on the country’s inflation trajectory. This political instability comes at a critical time for...
November 2024 Global Inflation Call: Transcript
Global Inflation Amid Trade Uncertainties Good afternoon and welcome to Turnleaf’s global inflation call. For the past month, global inflation expectations have been shaped by global trade uncertainty as proposed U.S. tariffs could hurt key global industries while...
Takeaways from QuantMinds 2024 in London
Over the past years, the quant industry has changed substantially. My first visit to Global Derivatives was just over a decade ago. At the time, perhaps unsurprisingly, the conference was dominated by presentations about option pricing. Over the years, the content has...
Macroeconomic Insights – Poland’s Fight with External and Domestic Demand
As Poland navigates a complex economic landscape, its rapid growth, fueled by competitive wages and strong manufacturing, faces challenges from both domestic and external pressures. The country’s success in attracting manufacturing investments has driven robust...
Takeaways from Web Summit 2024
Think of Lisbon and no doubt it’ll conjure images of explorers setting sail in centuries past across the ocean, the hills that climb across the city, pastel de nata and salted cod… Of course, there is much to Lisbon which cannot be summed in a sentence of...
Macroeconomic Insights: UK Autumn 2024 Budget and Global Trade Pressures Add to Inflation Challenges
The UK government's Autumn Budget for 2024, introduced on October 30, is designed to enhance public services through increased capital investments, funded by higher taxes along with adjustments in welfare and spending. The Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR)...